Erlang Calculator
Calculate the number of staff you need beforehand to ensure seamless workforce planning with our easy-to use Erlang C Calculator. Get the right number of people on the right tasks at the right time to offer your customers the best experience ever.
Tell us about your inbounds to calculate the required staffing
Your results
Surfers
Calls
Service level
Occupancy
Compute hourly staffing
Adjust the inbound volumes below to calculate hourly staffing
What is an Erlang calculator?
An Erlang calculator helps telecoms systems estimate the resources needed for a specific amount of traffic or workload. Call centres and customer support departments often use it to handle incoming requests or calls.
The Erlang calculator considers the traffic intensity (the average number of arrivals per unit of time), the average call duration, and the desired service level (usually expressed as the percentage of calls answered within a certain time threshold).
Based on these inputs, the calculator estimates the number of surfers required to handle the expected workload.
How to use an Erlang calculator for call centre staffing
- Suppose you want to determine how many surfers you need to handle the incoming calls in 1 hour. Historical data that tells you the average number of calls received per hour is 100, Your target service level is 5 minutes (0.083 hours). Your target service level is to answer at least 80% of calls within 20 seconds.
- Input these values and calculate the required number of surfers using an Erlang calculator.
- In this example, the Erlang calculator might tell you that you need 10 surfers to handle the incoming calls during that hour. With 10 surfers available, you can achieve your target service level by answering at least 80% of calls within 20 seconds.
Elements of the Erlang C formula:
- Pw = probability of a delay when the customer waits to connect with a surfer, P > 0
- A = total traffic (traffic intensity) of the call centre in Erlangs
- N = number of available call centre resources/agents
Assumptions of the Erlang C formula:
- The customer requests follow a Poisson Arrival Process (number of events over a given period).
- The number of customers is large.
- The impact of a single customer has minimal impact on the overall system performance.
- All customers use the system independently of others.
- Service times are exponentially distributed.
- Customers never abandon any service request while waiting for a support agent to respond
- All lost calls are not abandoned but simply delayed.
- A surfer handles only one customer exclusively for the specified period.
- The total number of support resources is lower than the number of customers.
Note
The Erlang C formula does not work if customer requests are non-independent or if they’re triggered by a common event, such as calling a helpline following a natural disaster. The formula usually provides acceptable results only if the number of customers is at least 10 times the number of agents.
Erlang C is relatively straightforward in application. The following is a run through of how to calculate it:
- Determine the number of call requests per hour.
- Compute the traffic intensity.
- Calculate call minutes based on AHT (usually in minutes) per request.
- Divide call minutes by 60 to compute call hours.
- Call hours refer to the intensity of traffic, measured in Erlangs.
- Determine the number of support surfers required to handle the traffic smoothly, with no waiting time. Each call occurs only after completing the previous one.
- Find the chance of delay by using the values you calculated and plugging them into the Erlang C formula.
- Surf the number of service surfers until you meet the desired service level.
Manually calculating Erlang C can be cumbersome and time-consuming. Save your time and use Surfboard’s integrated forecasting feature to get your answers in seconds.
Metrics for Erlang C
🔥 Traffic intensity
Traffic intensity is the average number of arrivals (e.g., calls, requests, customers) per unit of time. It is typically measured in Erlangs. The Erlang calculator requires this metric to understand the incoming workload and resource allocation.
⏱ Average call duration
This metric represents the average time to handle a single call or transaction. It is usually measured in seconds or minutes. The Erlang calculator uses the average call duration to estimate each surfer’s time on a call, influencing the number of resources required to handle the workload.
⭐️ Service level objective (SLA)
The service level objective defines the target level of service you want to achieve. It is often expressed as a percentage of calls answered within a certain time threshold. The Erlang calculator considers the service level objective to estimate the surfers needed to meet the desired service level.
🙅♀️ Blocking probability
Blocking probability is the possibility that an arriving call or request will be blocked or rejected due to insufficient surfers. It is a measure of how well the system can handle the workload. The Erlang calculator can provide you with an estimate of the blocking probability, which can help you evaluate your performance and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
👨👨👦👦 Number of resources
This metric refers to the available resources in your system that can handle the workload, such as surfers, servers, or lines. It allows finding the right balance between resource availability and service level targets. The Erlang calculator helps you determine the optimal resources required based on the above-mentioned metrics.
Erlang calculator spreadsheet template
Manual Erlang C calculators require you to input the relevant parameters and perform calculations manually. These calculators typically provide a set of formulas based on Erlang theory, such as the Erlang C formula. These calculators are usually available in spreadsheets.
To use a manual Erlang C calculator:
- Input the required parameters.
- Perform the calculations according to the provided Erlang C formulas.
- Interpret the results.
Download our free Erlang calculator spreadsheet template
Online and integrated Erlang calculators
Online Erlang C calculators are often found in web-based tools of workforce management (WFM) software and automate the calculation process for you. They are accessible through websites or software, like Surfboard, and offer a user-friendly interface.
Using an online Erlang C calculator is relatively simple:
- Enter the relevant parameters- traffic intensity, average call duration, and service level objective, into the provided fields.
- The calculator then processes the inputs using the underlying Erlang formulas.
- It generates the estimated surfers required to handle the workload.
Online calculators often provide additional features:
- Perform “what-if” analyses and scenario planning
- Reports and insights into arrival patterns
They are convenient and widely used as they eliminate the need for manual calculations and offer quick and accurate staffing requirements.
Explore Surfboard forecasting
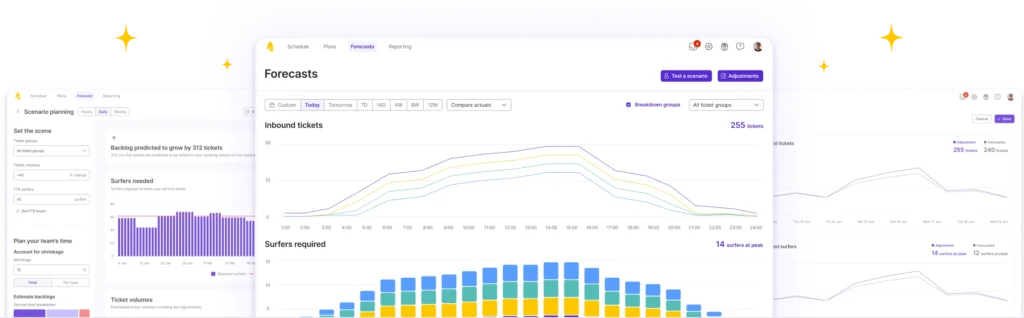
Surfboard’s integrates with 10+ ticketing and telephony systems, including Zendesk, Intercom, Dixa, Aircall and more, to automatically forecast expected ticket volumes. Produce detailed staffing requirements for every live and asynchronous channels with advanced configuration around shrinkage, productivity, concurrency and SLAs.
Learn how Hypervolt and Bloom & Wild improved staffing accuracy with Surfboard.
Book a demo to understand how Surfboard’s easy, integrated forecasting tools can streamline your support team and call centre scheduling.